The routing information protocol allows routers to determine what route is to be used to send the data.
Routing protocols allow routers to direct or route packets to different networks using tables.
There are static and dynamic routing protocols.
Static Routing Protocol: It is generated by the administrator, all static routes that have been entered in the router "will know", therefore, by routing packets to those networks.
Dynamic Routing Protocols: With a dynamic routing protocol, the administrator is only responsible for configuring the routing protocol through the IOS commands, in all routers in the network and these automatically exchange their routing tables with their neighboring routers, so Therefore, each router knows the network thanks to the publications of the other networks that it receives from other routers.
Two types of routing protocols
The Internet is made up of a large number of Autonomous Systems, which are networks that belong to a single administrative entity, with unified routing policies.
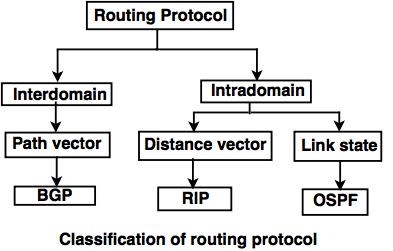 a.
a. Intradomain routing protocol: Within an autonomous system.
- Distance Vector
- Routing Information Protocol (RIP), Bellman-Ford based
- RIP is an internal routing protocol, that is, for the internal part of the network, which is not connected to the Internet backbone. It is widely used in internet connection systems such as infovia, in which many users connect to a network and can access through different places.
- Each router periodically exchange reachability information with its neighbors
- Minimal communication overhead
- Takes long to converge, i.e., in proportion to the maximum path length
- Link State
- Open Shortest Path First Protocol (OSPF), based on Dijkstra
- OSPF is used, as RIP, in the internal part of the networks, its way of functioning is quite simple. Each router knows the routers. In addition to this, each router knows at what distance. So you have to send a package sent by the route for which you have to give less jumps.
- Each router periodically floods immediate reachability information to other routers
- Fast convergence
- High communication and computation overhead
b. Interdomain routing protocol: between Autonomous Systems
- Use TCP for reliable transport
- Path vector protocol
- Routing messages indicate changes, no refreshes
- BGP routing information
- External gateway routing protocol by distance vector.
- The concept of Interior or Exterior Gateway, refers to the operation within an Autonomous system or outside it. An autonomous system, can be an organization that has all the control of its network, these autonomous systems are assigned an identification number by the ARIN (American Registry of Internet numbers), or by a service provider. Routing protocols such as IGRP and EIGRP, We need this number when configuring it.
- The BGP protocol is from the external Gateway, that is, it is outside the autonomous systems, usually between those that are located and the border routers between ISP, or between a company and an ISP, or between networks that interconnect countries.
